
SONiC is a subproject within the Open Compute Foundation https://www.opencompute.org/wiki/Networking/SONiC. Networking industry has primarily been operating similar to mainframes, i.e. you buy your hardware and software from the same vendor. Over the last decade we have been seeing the rise of disaggregated models where the end users could purchase hardware from a vendor but run software from another vendor. In this post we will do an introduction to SONiC and attempt to get kick started with setting up a connectivity between two devices running the SONiC NOS and perform connectivity testings.
For the testing portion we will use SONiC-P4 software switch which runs on a P4-emulated SAI. This will allow us to run SONiC in a container without needing to deploy the SONiC on a real switch.
What is SONiC?
From the SONiC main page https://azure.github.io/SONiC/, SONiC is an open source network operating system based on Linux that runs on switches from multiple vendors and ASICs. SONiC offers a full-suite of network functionality, like BGP and RDMA, that has been production-hardened in the data centers of some of the largest cloud-service providers. It offers teams the flexibility to create the network solutions they need while leveraging the collective strength of a large ecosystem and community.
SONiC is based on Debian Jessie, it has also been ported Ubuntu as snap. A growing list devices and platforms are currently supported, this list can be found at https://github.com/Azure/SONiC/wiki/Supported-Devices-and-Platforms. Most datacenter ASIC vendors are covered in the list such as Broadcom, Mellanox, Innovium etc.
SONiC-P4 Software Switch
SONiC-P4 is a software switch that runs on the P4-emulated SAI behavioral model software switch ASIC. Code for this maintained by Mellanox under https://github.com/Mellanox/SAI-P4-BM. It uses the sai_bm.p4 to program the P4-emulated switch ASIC to emulate the data plane behavior. On top of that, it runs the real SONiC network stack. The current SONiC-P4 is released as a docker image.
Assumptions
In our setup we will be installing SONiC docker image on a Ubuntu 16.04 running Docker CE.
$ lsb_release -a
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Ubuntu
Description: Ubuntu 16.04.6 LTS
Release: 16.04
Codename: xenial
$ nproc
2
$ free -m
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 7903 296 6724 17 883 7298
Swap: 0 0 0Topology
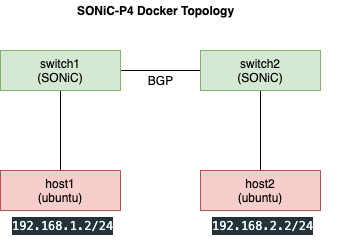
The switches switch1 and switch2 are running SONiC NOS and have host1 and host2 connected to them respectively. The swtiches are in two different BGP ASN and peer with each other.
switch1 - announces 192.168.1.0/24 via BGP
switch2 - announces 192.168.2.0/24 via BGP
Installing SONiC-P4 on Ubuntu 16.04 via docker
First download SONiC P4 software.
$ wget https://github.com/Azure/SONiC/wiki/files/SONiC-P4/SONiC-P4.Test.tar.gz
--2020-06-21 21:44:30-- https://github.com/Azure/SONiC/wiki/files/SONiC-P4/SONiC-P4.Test.tar.gz
Resolving github.com (github.com)... 140.82.118.4
Connecting to github.com (github.com)|140.82.118.4|:443... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 302 Found
Location: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wiki/Azure/SONiC/files/SONiC-P4/SONiC-P4.Test.tar.gz [following]
--2020-06-21 21:44:30-- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wiki/Azure/SONiC/files/SONiC-P4/SONiC-P4.Test.tar.gz
Resolving raw.githubusercontent.com (raw.githubusercontent.com)... 199.232.24.133
Connecting to raw.githubusercontent.com (raw.githubusercontent.com)|199.232.24.133|:443... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 3361 (3.3K) [application/octet-stream]
Saving to: 'SONiC-P4.Test.tar.gz'
SONiC-P4.Test.tar.gz 100%[===================================================================================================================>] 3.28K --.-KB/s in 0s
2020-06-21 21:44:30 (47.3 MB/s) - 'SONiC-P4.Test.tar.gz' saved [3361/3361]
Next extract tar file and then cd to p4-test/ folder
$ tar xvf SONiC-P4.Test.tar.gz
p4-test/
p4-test/load_image.sh
p4-test/test.sh
p4-test/switch2/
p4-test/switch2/scripts/
p4-test/switch2/scripts/startup.sh
p4-test/switch2/etc/
p4-test/switch2/etc/quagga/
p4-test/switch2/etc/quagga/zebra.conf
p4-test/switch2/etc/quagga/bgpd.conf
p4-test/switch2/etc/quagga/daemons
p4-test/switch2/etc/swss/
p4-test/switch2/etc/swss/config.d/
p4-test/switch2/etc/swss/config.d/00-copp.config.json
p4-test/switch2/etc/config_db/
p4-test/switch2/etc/config_db/vlan_config.json
p4-test/stop.sh
p4-test/start.sh
p4-test/install_docker_ovs.sh
p4-test/switch1/
p4-test/switch1/scripts/
p4-test/switch1/scripts/startup.sh
p4-test/switch1/etc/
p4-test/switch1/etc/quagga/
p4-test/switch1/etc/quagga/zebra.conf
p4-test/switch1/etc/quagga/bgpd.conf
p4-test/switch1/etc/quagga/daemons
p4-test/switch1/etc/swss/
p4-test/switch1/etc/swss/config.d/
p4-test/switch1/etc/swss/config.d/00-copp.config.json
p4-test/switch1/etc/config_db/
p4-test/switch1/etc/config_db/vlan_config.json
$ cd p4-test/Now we need to run ./install_docker_ovs.sh. This will install docker and OpenvSwitch
$ ./install_docker_ovs.shNext we will grab latest build for SONiC P4 and then load this imagine in to docker
wget wget https://sonic-jenkins.westus2.cloudapp.azure.com/job/p4/job/buildimage-p4-all/613/artifact/target/docker-sonic-p4.gz
$ docker load < docker-sonic-p4.gz
ffc4c11463ee: Loading layer [==================================================>] 129.3MB/129.3MB
6bae7e0e696e: Loading layer [==================================================>] 77.94MB/77.94MB
483897c390a9: Loading layer [==================================================>] 51.87MB/51.87MB
dc77b88bb913: Loading layer [==================================================>] 204MB/204MB
Loaded image: docker-sonic-p4:latest
Now will run start.sh script. This script will run the neccessary docker containers and configure OVS to enable networking between the SONiC emulated switches.
$ ./start.sh
79a1e4d5b2ae27d890f803626c5dd3b40331f0d01294de0a313a0d4db2e9a41b
29f3f3deecc2b7cd4e39dae95113fce425ae0f94270f6885d52292abf66b6c24
Unable to find image 'ubuntu:14.04' locally
14.04: Pulling from library/ubuntu
2e6e20c8e2e6: Pull complete
30bb187ac3fc: Pull complete
b7a5bcc4a58a: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:ffc76f71dd8be8c9e222d420dc96901a07b61616689a44c7b3ef6a10b7213de4
Status: Downloaded newer image for ubuntu:14.04
1bac133b9073984aba69cdfd7d5320ef84823bbe3a503f06bddc88d7452750b0
f798c20e0f817af7119d00c54dc005a4221dfdcd2e311768d6619cfbbd3b4d79
Booting switches, please wait ~1 minute for switches to loadNow let’s run docker ps to see what containers are running
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
51a210aea570 ubuntu:14.04 "/bin/bash" 12 minutes ago Up 12 minutes host2
0ae5eca58d9b ubuntu:14.04 "/bin/bash" 12 minutes ago Up 12 minutes host1
3697ce9bd41a docker-sonic-p4:latest "/bin/bash" 12 minutes ago Up 12 minutes switch2
663d6a66eed3 docker-sonic-p4:latest "/bin/bash" 12 minutes ago Up 12 minutes switch1We can see that we have four containers running, two hosts and two switches.
We are now going to run a test that will ping from host2 to host1
$ ./test.sh
PING 192.168.2.2 (192.168.2.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.2.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=62 time=9.81 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.2.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=62 time=14.9 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.2.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=62 time=8.42 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.2.2: icmp_seq=4 ttl=62 time=14.7 msIn the next part we check th eBGP sessions between the SONiC switches. The routing daemon used on the P4-switch is Quagga. To check the eBGP session we need to SSH to docker image for switch1 by using docker exec command. This will allow us to run vtysh commands to check BGP adjacency.
$ docker exec -it switch1 bash
root@663d6a66eed3:/#
root@663d6a66eed3:~# vtysh -c "show ip bgp sum"
BGP router identifier 192.168.1.1, local AS number 10001
RIB entries 3, using 336 bytes of memory
Peers 1, using 4656 bytes of memory
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
10.0.0.1 4 10002 380 384 0 0 0 00:06:18 1
Total number of neighbors 1Startup scripts
There are couple important startup scripts used for the this emulated setup. The start.sh and switch1\scripts\startup.sh. The first one is responsible creating networking between switch1 and switch2 docker containers. This would be similar to cabling up switches if you had real switches. The later script is responsible for configuring the SONiC switches.
Docker startup script
$ cat start.sh
#!/bin/bash
sudo docker run --net=none --privileged --entrypoint /bin/bash --name switch1 -it -d -v $PWD/switch1:/sonic docker-sonic-p4:latest
sudo docker run --net=none --privileged --entrypoint /bin/bash --name switch2 -it -d -v $PWD/switch2:/sonic docker-sonic-p4:latest
sudo docker run --net=none --privileged --entrypoint /bin/bash --name host1 -it -d ubuntu:14.04
sudo docker run --net=none --privileged --entrypoint /bin/bash --name host2 -it -d ubuntu:14.04
sudo ovs-vsctl add-br switch1_switch2
sudo ovs-docker add-port switch1_switch2 sw_port0 switch1
sudo ovs-docker add-port switch1_switch2 sw_port0 switch2
sudo ovs-vsctl add-br host1_switch1
sudo ovs-docker add-port host1_switch1 sw_port1 switch1
sudo ovs-docker add-port host1_switch1 eth1 host1
sudo ovs-vsctl add-br host2_switch2
sudo ovs-docker add-port host2_switch2 sw_port1 switch2
sudo ovs-docker add-port host2_switch2 eth1 host2
sudo docker exec -d host1 sysctl net.ipv6.conf.eth0.disable_ipv6=1
sudo docker exec -d host1 sysctl net.ipv6.conf.eth1.disable_ipv6=1
sudo docker exec -d host2 sysctl net.ipv6.conf.eth0.disable_ipv6=1
sudo docker exec -d host2 sysctl net.ipv6.conf.eth1.disable_ipv6=1
sudo docker exec -d host1 ifconfig eth1 192.168.1.2/24 mtu 1400
sudo docker exec -d host1 ip route replace default via 192.168.1.1
sudo docker exec -d host2 ifconfig eth1 192.168.2.2/24 mtu 1400
sudo docker exec -d host2 ip route replace default via 192.168.2.1
sudo docker exec -d switch1 ip netns add sw_net
sudo docker exec -d switch1 ip link set dev sw_port0 netns sw_net
sudo docker exec -d switch1 ip netns exec sw_net sysctl net.ipv6.conf.sw_port0.disable_ipv6=1
sudo docker exec -d switch1 ip netns exec sw_net ip link set sw_port0 up
sudo docker exec -d switch1 ip link set dev sw_port1 netns sw_net
sudo docker exec -d switch1 ip netns exec sw_net sysctl net.ipv6.conf.sw_port1.disable_ipv6=1
sudo docker exec -d switch1 ip netns exec sw_net ip link set sw_port1 up
sudo docker exec -d switch2 ip netns add sw_net
sudo docker exec -d switch2 ip link set dev sw_port0 netns sw_net
sudo docker exec -d switch2 ip netns exec sw_net sysctl net.ipv6.conf.sw_port0.disable_ipv6=1
sudo docker exec -d switch2 ip netns exec sw_net ip link set sw_port0 up
sudo docker exec -d switch2 ip link set dev sw_port1 netns sw_net
sudo docker exec -d switch2 ip netns exec sw_net sysctl net.ipv6.conf.sw_port1.disable_ipv6=1
sudo docker exec -d switch2 ip netns exec sw_net ip link set sw_port1 up
echo "Booting switches, please wait ~1 minute for switches to load"
sudo docker exec -d switch1 sh /sonic/scripts/startup.sh
sudo docker exec -d switch2 sh /sonic/scripts/startup.shSONiC switch configuration script
This script copies the following configuration files to initialise the switch configuration. The main configuration files that copied over are
- config_db.json (This is the main switch configuration, equivalent to running-config in Cisco world)
- default_config.json (SWitch State Service - SWSS)
- quagga (Routing daemon)
- bgpd.conf
- daemons
- zebra.conf
$ cat switch1/scripts/startup.sh
[ -d /etc/sonic ] || mkdir -p /etc/sonic
SYSTEM_MAC_ADDRESS=00:01:04:4c:49:f5
ip link add eth0 addr $SYSTEM_MAC_ADDRESS type dummy
if [ -f /etc/sonic/config_db.json ]; then
sonic-cfggen -j /etc/sonic/config_db.json -j /sonic/scripts/vlan_config.json --print-data > /tmp/config_db.json
mv /tmp/config_db.json /etc/sonic/config_db.json
else
sonic-cfggen -j /sonic/etc/config_db/vlan_config.json --print-data > /etc/sonic/config_db.json
fi
#chmod +x /usr/bin/config_bm.sh # TODO: remove this line
cp -f /sonic/etc/swss/config.d/00-copp.config.json /etc/swss/config.d/default_config.json
cp -rf /sonic/etc/quagga /etc/
ip netns exec sw_net ip link set dev sw_port0 addr $SYSTEM_MAC_ADDRESS
ip netns exec sw_net ip link set dev sw_port1 addr $SYSTEM_MAC_ADDRESSSONiC configuration
SONiC manages its configuration in a redisDB that is referred to as ConfigDB. Applications subscribe to ConfigDB and generate their running configuration correspondingly. In current version of SONiC, ConfigDB is implemented as database 4 of local redis. When system boots, configurations will be loaded from /etc/sonic/config_db.json file into redis.
CLI commands
SONiC has CLI commands similar to Arista, Juniper and Cisco. Whilst these commands are available on the SONiC-P4 Software Switch, this requires sudo which is not available in the docker images. Also it looks like these show and config are just Linux aliases to configure or retrieve information.
Below are some sample show commands that are available through CLI.
root@ff52ddd9863a:/# show
Usage: show [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
SONiC command line - 'show' command
Options:
-?, -h, --help Show this message and exit.
Commands:
aaa Show AAA configuration in ConfigDb
acl Show ACL related information
arp Show IP ARP table
clock Show date and time
ecn Show ECN configuration
environment Show environmentals (voltages, fans, temps)
interfaces Show details of the network interfaces
ip Show IP (IPv4) commands
ipv6 Show IPv6 commands
lldp LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol)...
logging Show system log
mac Show MAC (FDB) entries
ntp Show NTP information
platform Show platform-specific hardware info
processes Display process information
runningconfiguration Show current running configuration...
services Show all daemon services
session Show existing everflow sessions
startupconfiguration Show startup configuration information
system-memory Show memory information
tacacs Show TACACS+ configuration
techsupport Gather information for troubleshooting
uptime Show system uptime
users Show users
version Show version information
vlan Show VLAN informationSimilarly these are config commands that available through CLI.
root@ff52ddd9863a:/# config
Usage: config [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
SONiC command line - 'config' command
Options:
--help Show this message and exit.
Commands:
aaa AAA command line
acl ACL-related configuration tasks
bgp BGP-related configuration tasks
ecn ECN-related configuration tasks
interface Interface-related configuration tasks
load Import a previous saved config DB dump file.
load_mgmt_config Reconfigure hostname and mgmt interface based...
load_minigraph Reconfigure based on minigraph.
qos
reload Clear current configuration and import a...
save Export current config DB to a file on disk.
tacacs TACACS+ server configuration
vlan VLAN-related configuration tasks